Learn more about Registers in the context of PSD2 XS2A.
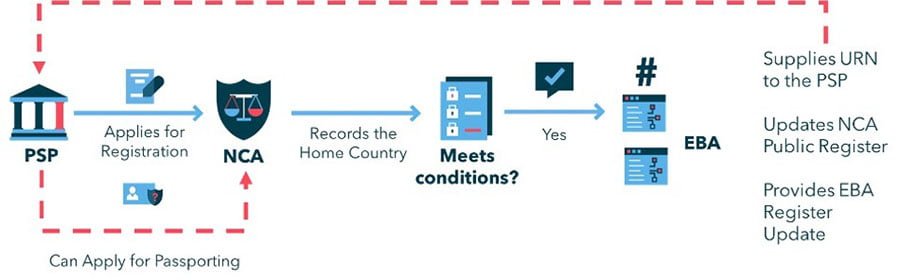
Entities that want to provide Payment Services as a Payment Services Provider (PSP) must first apply to their Home National Competent Authority (NCA). Once authorised, they take on the appropriate Payment Services Roles & are issued with a Unique Reference Number (URN). The URNs and authorisations are published in National Registers & may also be found in the EBA Registers.
Payment Service Providers (PSPs) PSD1 and PSD2 defines six categories of Regulated Entity that can register with their Home NCA to provide payment services and become PSPs:
- Credit Institutions
- Payment Institutions
- Electronic Money Institutions
- Central Banks
- Post Office Giro Institutions (in some countries)
- Government Ministries (in some countries)
Additionally, there are a number of additional Access To Account (XS2A) payment services set out in PSD2:
- Payment Initiation Service Providers (PISPs), who perform Payment Initiation Services (PIS)
- Account Information Service Providers (AISPs), who perform Account Information Services (AIS)
- Card Based Payment Instruments Issuing Providers (CBPIIPs), who perform Card Based Payment Instruments Issuing Services (CBPII)
Collectively, these 3 PSPs are called Third Party Providers (TPPs). TPPs rely on other PSPs to enable access to customer accounts/data for the provision of XS2A services. The PSPs who provide and operate customer accounts and enable this access are called Account Servicing Payment Service Providers (ASPSPs).
XS2A Payment Services & Roles
Entities that want to provide an XS2A service must first be a category of PSP that already has or obtains the right to perform specific payment services, and so inherits the right to perform the related service roles:
| PSP Category | Payment Service | Role |
|---|---|---|
| Entity applies to be (or already is) one of the following categories… | PSP applies to provide one or more of the following services… | Once authorised, the PSP plays the following role… |
|
(Payment Initiation Services (PIS) Account Information Services (AIS) Card Based Payment Instruments Issuing (CBPII) PSPs that operate payment accounts and allow online access |
Payment Initiation Becomes a Payment Initiation Services Provider (PISP) Account Information Becomes an Account Information Services Provider (PISP) Card Based Payment Instruments Becomes a Card Based Payment Instruments Provider (CBPIIP) Account Servicing Becomes an Account Servicing Payment Services Provider (ASPSP) |
Exempted PSPs cannot be granted authorisation for PIS or AIS roles without applying to become one of the permitted PSP categories first. Credit Institutions can automatically have all of the roles without further registration.
National Competent Authorities
In each European Union (EU) and European Economic Area (EEA) Member State, there is a single NCA which has been designated to oversee the country’s financial supervision
NCAs are responsible for the financial supervision of payment services in their country, including:
- Processing & Decision Making
- Management & Maintenance
- Maintenance (Including De-Authorisation)
- In-Country Reporting Collection In-Country Dispute Management
- In-Country Incident Management
- National Reporting & Communications
- Cross-Border Communications
As only one NCA is designated for each country under PSD2, it is clear which NCA represents each country’s financial system, so there is no confusion as to whether a PSP is authorised or not in a specific country.
Registration & Passporting
PSPs register with, and apply to, their Home NCA for the appropriate payment services authorisations. Once a PSP has obtained the authorisations and holds the payment service roles required, they then need to apply for passporting rights to provide the services for which they are authorised throughout the EU.
This content was originally published in May 2021 for participants of the Open Banking Exchange Membership Programme. It consisted of the Open Banking Exchange’ sole opinion as of its date of publication and was intended for general information of its members. It is now available for visitors to the Konsentus website. To access this content, please complete the form below.
Unique Reference Numbers
When a PSP is authorised to perform payment services, their Home NCA issue identification numbers, known as Authorisation Numbers, so they can be uniquely identified apart from other PSPs. Some NCAs use existing numbers such as a LEI, VAT Number or a Company Number as the Authorisation number, others generate a new number. Additionally, NCAs may use different names in the Authorisation Numbers. Confusingly, many NCAs also have other numbers that are NOT the National Identification Number, Legal Entity Identifier, Registration Number, and “other Equivalent means of identification.” For simplicity, OBE refers to Authorisation Numbers as Unique Reference Numbers (URNs). Because many countries issue 5 digit URNs, they do not uniquely identify regulated entities across countries. To make them unique, OBE created Global-Unique Reference Numbers (G-URNs). G-URNs are constructed by combining:
The Country Code + The NCA Code + The Unique Reference Number
For example, the code SE-FI-45002 is the G-URN for Trustly in Sweden
The G-URN standard was created by Open Banking Europe and has been adopted by the ETSI for their certificates.
The National Registers
The NCAs provide lists, called National Public Registers, of all the PSP categories and the payment services and roles that PSPs are authorised to perform. Each Register records the registration, payment services authorisations, passporting, and other status details for every PSP in the country. The data required includes:
- Home Country & Address ▪ Unique Reference Number (URN)
- Authorisation/Registration Status
- Payment Service Roles Authorised
- Country Permissions for Each Authorised Role
ASPSPs can use the National Registers to verify that those TPPs who request access to their customer accounts have been granted the appropriate and relevant payment services and roles required for access. National Registers can be hard to read without specialist knowledge and local language skills as they:
- Are all in their own format
- Use their own terminology
- Often contain a register for each PSP category
- Can be in their own language
- Are almost never machine readable
- Often contain multiple Identification Numbers
The EBA Register
Under PSD2, the EBA is required to make publicly available a list of all registered PSPs in the EU by aggregating information from the 31 National Registers. However, as has been observed, the data contained within the EBA Register may not be reflective of the 31 National Registers. There are actually two EBA Registers available, each containing different sets of regulatory information:
The Payment Institutions Register which contains:
- Payment Institutions
- E-money Institutions
- Exempted Institutions
- Agents
- Branches
- Service Providers excluded from PSD2
The Credit Institutions Register which contains:
- CRD Credit Institutions
- EEA Branches
- Non EEA Branches
The EBA Registers should not be used a way to verify TPPs for XS2A as:
- There is no single source of Regulatory Data, (two different registers with different purposes)
- There are Authorisation Number issues (missing numbers, mismatches, formatting issues).
- Manual search is available only, but no download function and only partial machine readability.
- The Registers clearly state the primacy of the NCA Public Registers for TPP checking.
- There are no notifications on data changes & no version history to check historic change.
- Updates to the Registers are irregular, i.e. not always occurring daily.
To learn more about Registers in the context of PSD2 XS2A and to find out more about Konsentus’ technology solutions, get in touch with a member of our team.